M1A1 Abrams Main Battle Tank (BAG 2)
As the Gulf War shifted pace from Operation Desert Shield to Operation Desert Storm, and the preparatory bombardment lifted, U.S. Abrams tanks spearheaded the attack on Iraqi fortifications and engaged enemy tanks whenever and wherever possible. Just as they had done in the Iran-Iraq War, the Iraqi Army used it's tanks as fixed anti-tank and artillery pieces, digging them into the ground to reduce target signature. However, this also prevented their quick movement and Allied air power smashed nearly 50% of Iraq's tank threat before Allied armor had moved across the border. After that the Abrams tanks quickly destroyed a number of Iraqi tanks that did manage to go mobile.
The Abrams' thermal sights were unhampered by the clouds of thick black smoke over the battlefield that were the result of burning Kuwaiti oil wells. In fact many Gunners relied on their "night" sights in full daylight. Such was not the case with the sights in the Iraqi tanks, which were being hit from units they could not even see. Concerns about the M1A1's range were eliminated by a massive resupply operation that will be studied for years as a model of tactical efficiency.
During the Gulf War only 18 Abrams tanks were taken out of service due to battle damage: nine were permanent losses, and another nine suffered repairable damage, mostly from mines. Not a single Abrams crewman was lost in the conflict. There were few reports of mechanical failure. US armor commanders maintained an unprecedented 90% operational readiness for their Abrams Main Battle Tanks.
Specifications | |||
| M1 / IPM1 | M1A1 | M1A2 | |
| Manufacturer | General Dynamics (Land Systems Division) | ||
| Crew | 4: Commander, Gunner, Loader & Driver | ||
| Weight | 60 Tons | 63 Tons | 69.54 Tons |
| Length (Gun Forward) | 384.5 inches | 387 inches | |
| Turret Height | 93.5 inches | ||
| Width | 143.8 inches | 144 inches | |
| Ground Clearance | 19 inches | ||
| Ground Pressure | 13.1 PSI | 13.8 PSI | 15.4 PSI |
| Obstacle Crossing | 49 inches | 42 inches | |
| Vertical Trench | 9 Feet | ||
| Power plant | AGT-1500 turbine engine | ||
| Power Rating | 1500 HP | ||
| Power to Weight Ratio | 25 hp/ton | 23.8 hp/ton | 21.6 hp/ton |
| Hydro Kinetic Transmission | 4 Speed Forward 2 Speed Reverse | ||
| Speed - Maximum | 45 mph (Governed) | 42 mph (Governed) | |
| Speed - Cross Country | 30 mph | ||
| Speed - 10% Slope | 20 mph | 17 mph | |
| Speed - 60% Slope | 4.5 mph | 4.1 mph | |
| Acceleration (0 to 20 mph) | 7 Seconds | 7.2 Seconds | |
| Cruising Range | 275 Miles | 265 Miles | |
| Main Armament | 105mm M68A1 Rifled Cannon | 120mm M256 Smooth Bore Cannon | |
| Commander's Weapon | .50 Cal M2 Machinegun | ||
| Coaxial Weapon | 7.62 M240 Machinegun | ||
| Loader's Weapon | 7.62 M240 Machinegun on Skate Mount | ||
| NBC System | 200 SCFM - CleanCooled Air | ||
| Inventory | 403 USMC | ||
| Unit Replacement Cost | $4,300,000 | ||
M1 / IPM1 Abrams Main Battle Tank
Designed in the 1970's by the Land Systems Division of the General Dynamics Corporation in response to the U.S. Army's MBT-70 program, the first M1 rolled off the assembly line in 1978. After two years of acceptance trials, the first of these vehicles was delivered to the US Army on February 28, 1980. By 1985, evaluations of field service had prompted the first modification requests, and production shifted to the M1A1. The first M1A1's were delivered to units in August of 1985. The Army has converted 368 older M1s to M1A2s. An additional 580 M1s are being upgraded to A2s under a five-year contract awarded in FY1996, with a total of 998 M1 upgrades planned. In 1999 the Army began upgrading M1s to the M1A2 System Enhancement Program (SEP) configuration. The SEP embeds digitization capabilities inside the Abrams' electronic architecture, eliminating the requirement for electronic appliques.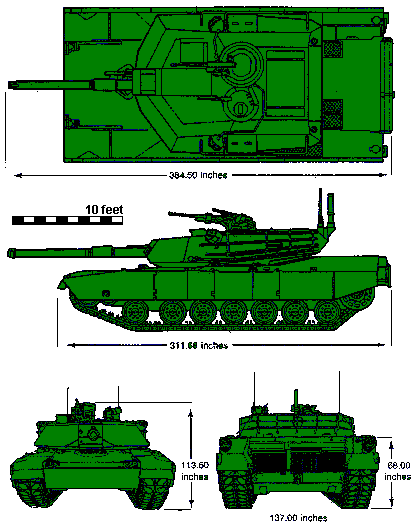







0 komentar
Write Down Your Responses